Imagine generating your own clean electricity, reducing your reliance on the grid, and shrinking your carbon footprint, all powered by the wind in your own backyard. For homeowners seeking energy independence and a greener lifestyle, wind energy presents an intriguing possibility.
Choosing the right wind turbine is crucial to maximizing energy production and return on investment. Understanding the fundamental differences between vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) and horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) will allow you to make an informed decision tailored to your specific property and energy needs.
Before diving into the specifics, consider your local wind resources. Investigate average wind speeds and prevailing wind directions in your area. This crucial first step will significantly impact the performance and suitability of either a VAWT or a HAWT system for your home.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines: Which is Right for Your Home?
Wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of the wind and convert it into electricity. While both VAWTs and HAWTs achieve this, their designs, performance characteristics, and suitability for different environments vary considerably. Understanding these distinctions is essential for homeowners considering adopting small wind energy for homes.
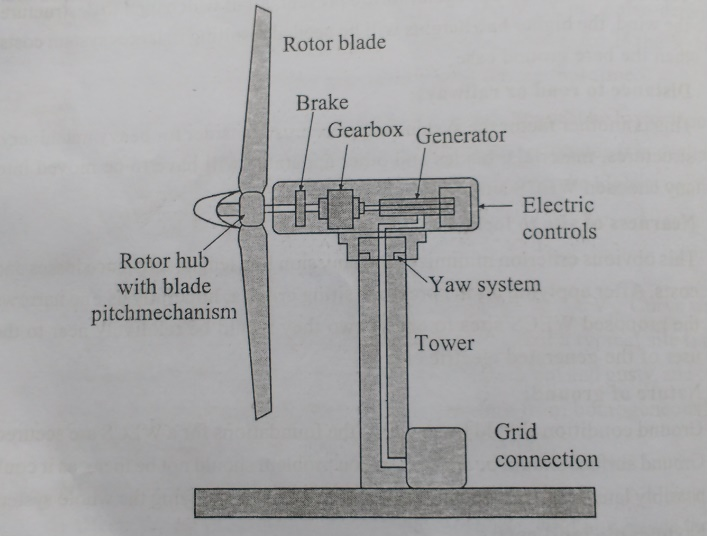
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs): The Traditional Design
HAWTs are the most recognizable type of wind turbine, characterized by their propeller-like blades rotating around a horizontal axis. These are the turbines you typically see in large wind farms.
Key Features:
High Efficiency: HAWTs generally boast higher efficiency than VAWTs in ideal conditions, capturing more energy from the wind.
Upwind vs. Downwind Designs: Upwind turbines face the wind directly, requiring a tail or yaw mechanism to track wind direction. Downwind turbines are positioned so the wind passes the tower before hitting the blades.
Tower Requirement: HAWTs require tall towers to access stronger, less turbulent winds at higher altitudes. Pros:
Higher Energy Output: Generally produce more electricity for a given rotor size.
Established Technology: Well-established technology with readily available components and expertise. Cons:
Aesthetics: Can be visually imposing and may not be suitable for all neighborhoods due to their size.
Noise: Can generate noise that may be a concern for nearby residents.
Complex Installation: Requires professional installation and specialized equipment.
Wind Direction Sensitivity: Requires a yaw mechanism to constantly face the wind, adding complexity and maintenance.
Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs): The Alternative Approach
VAWTs feature blades that rotate around a vertical axis. This design offers some unique advantages, particularly for residential applications.
Key Features:
Omnidirectional: VAWTs accept wind from any direction, eliminating the need for a yaw mechanism.
Ground-Level Installation: Can be installed closer to the ground, reducing tower requirements and installation costs.
Two Main Types:
Darrieus Turbines: Eggbeater-shaped blades, known for efficiency but often require external power to start.
Savonius Turbines: S-shaped scoops that catch the wind, providing high torque and self-starting capabilities. Pros:
Aesthetics: Often considered more aesthetically pleasing than HAWTs, with a modern, sculptural appearance.
Lower Noise: Generally quieter than HAWTs.
Simpler Installation: Easier to install and maintain due to their simpler design and ground-level accessibility.
Accepts Turbulent Winds: Performs better in turbulent wind conditions often found in urban or suburban environments. Cons:
Lower Efficiency: Generally less efficient than HAWTs in ideal conditions.
Lower Energy Output: Produces less electricity for a given rotor size compared to HAWTs.
Durability Concerns: Some designs can be prone to stress and fatigue in high winds.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Wind Turbine
Selecting the right wind turbine for your home requires careful consideration of several factors: Wind Resource: Assess the average wind speed and turbulence at your location. Areas with consistent, high wind speeds favor HAWTs, while VAWTs can be more effective in areas with variable or turbulent winds. Energy Needs: Determine your household's energy consumption. Calculate the amount of electricity you need to generate to offset your grid usage or achieve energy independence. Budget: Establish a realistic budget for the entire project, including the turbine, installation, permits, and maintenance. Home wind turbine cost varies dramatically based on turbine size and complexity. Zoning Regulations and Permits: Research local zoning regulations and permit requirements for wind turbine installation. Some jurisdictions have restrictions on turbine height, noise levels, and aesthetics. Property Size and Layout: Consider the size and layout of your property. HAWTs require more open space and taller towers, while VAWTs can be installed in smaller areas. Aesthetics: Think about the visual impact of the turbine on your property and neighborhood. Choose a design that complements your home and surroundings. Noise Levels: Research the noise levels of different turbine models and consider the proximity of your neighbors. Maintenance Requirements: Understand the maintenance requirements of each turbine type and factor in the cost of regular inspections and repairs. DIY Wind Power vs. Professional Installation:While DIY wind power projects can save money, professional wind turbine installation ensures safety, efficiency, and compliance with local regulations.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Rural Homeowner with Acreage (HAWT): A homeowner in a rural area with ample open space and consistent winds installed a 10k W HAWT on a 100-foot tower. The system generates enough electricity to offset their entire grid usage, resulting in significant savings on their electricity bill. The initial investment was approximately $50,000, but the homeowner qualified for federal tax credits and state rebates, reducing the overall cost. Suburban Resident with Limited Space (VAWT): A homeowner in a suburban neighborhood with limited space and variable winds installed a 2k W VAWT on their roof. While the system doesn't generate as much electricity as a HAWT, it provides a supplemental source of power and reduces their reliance on the grid. The installation was relatively straightforward and cost around $15,000. Off-Grid Living (Hybrid System):A family living off-grid in a remote location uses a hybrid system consisting of a 5k W HAWT and a solar panel array. The wind turbine provides a reliable source of power during windy periods, while the solar panels generate electricity during sunny days. The system is backed up by a battery bank to store excess energy for use during periods of low wind and sunshine.
People Also Ask:
What is the average lifespan of a home wind turbine?
The lifespan of a home wind turbine typically ranges from 20 to 30 years with proper maintenance. Factors such as wind conditions, turbine quality, and maintenance frequency can affect the lifespan. Regular inspections and timely repairs are crucial for maximizing the turbine's longevity.
How much electricity can a home wind turbine generate?
The amount of electricity a home wind turbine can generate depends on several factors, including turbine size, wind speed, and location. A small residential turbine (1-10 k W) can generate anywhere from a few hundred kilowatt-hours (k Wh) to several thousand k Wh per year. Consult with a wind energy professional to estimate the potential energy production for your specific location and turbine model.
Are there any government incentives for installing a home wind turbine?
Yes, many governments offer incentives for installing renewable energy systems, including home wind turbines. These incentives may include federal tax credits, state rebates, and local grants. Check with your federal, state, and local government agencies for available programs and eligibility requirements. The Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE) is a great resource for finding incentives in your area.
DIY Wind Turbine Considerations
Embarking on a DIY wind turbine project can be a rewarding experience, providing a hands-on approach to renewable energy generation. However, it's crucial to approach such projects with careful planning, technical expertise, and a strong emphasis on safety.
Research and Planning: Thoroughly research different DIY wind turbine designs and choose one that suits your skills and resources. Develop a detailed plan that includes materials list, construction steps, and safety precautions. Technical Skills: Possess the necessary technical skills in areas such as electrical wiring, welding, and mechanical assembly. If you lack experience in these areas, consider taking relevant courses or seeking guidance from experienced professionals. Safety Precautions: Prioritize safety at all times. Wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves, eye protection, and a hard hat. Work with a helper and follow all safety guidelines provided by the turbine manufacturer or design plans. Permitting and Regulations: Check local zoning regulations and permit requirements before starting your DIY wind turbine project. Ensure that your project complies with all applicable codes and regulations. Component Sourcing: Source high-quality components from reputable suppliers. Consider using salvaged or recycled materials where possible to reduce costs and environmental impact. Professional Consultation: Consult with a wind energy professional or electrical engineer to review your plans and provide guidance on safety and performance. Testing and Monitoring:After installation, thoroughly test the turbine and monitor its performance. Make any necessary adjustments to optimize energy production.
Maintaining Your Wind Turbine
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term performance and reliability of your home wind turbine. Develop a maintenance schedule and perform regular inspections to identify and address potential problems before they escalate.
Visual Inspections: Conduct regular visual inspections of the turbine blades, tower, and electrical components. Look for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Blade Cleaning: Clean the turbine blades periodically to remove dirt, dust, and debris that can reduce efficiency. Lubrication: Lubricate moving parts, such as bearings and gears, according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Bolt Tightening: Check and tighten all bolts and fasteners to prevent loosening due to vibration. Electrical System Check: Inspect the electrical wiring, connections, and grounding system for any signs of damage or deterioration. Professional Servicing: Schedule professional servicing at least once a year. A qualified technician can perform a thorough inspection, diagnose any potential problems, and perform necessary repairs or maintenance.
Choosing between a vertical axis wind turbine and a horizontal axis wind turbine for your home is a personal decision that depends on your specific needs and circumstances. By carefully evaluating your wind resource, energy needs, budget, and local regulations, you can make an informed choice and harness the power of the wind to generate clean, sustainable energy for your home. With the right turbine and proper maintenance, you can enjoy the benefits of wind energy for years to come.